

- #SERIAL VS PARALLEL DILUTION HOW TO#
- #SERIAL VS PARALLEL DILUTION SERIAL NUMBERS#
- #SERIAL VS PARALLEL DILUTION SERIAL#
- #SERIAL VS PARALLEL DILUTION PC#
- #SERIAL VS PARALLEL DILUTION SERIES#
Serial dilutions are widely used in experimental sciences, including biochemistry, pharmacology, microbiology, and physics. Serial dilutions are used to accurately create extremely diluted solutions, as well as solutions for experiments that require a concentration curve with an exponential or logarithmic scale. For example, a ten-fold serial dilution could result in the following concentrations: 1 M, 0.1 M, 0.01 M, 0.001 M, and so on. Serial dilutions involve diluting a stock or standard solution multiple times in a row. From one reading, determine the mean, SD, and SEM for the four replicates of the last (row C) of your serial dilutions.Examples of serial dilution in the following topics:. Are they significantly different? If so, what are the possible explanations for the discrepancy? When at least 4 students have written their results on the blackboard, find the highest and lowest. Write the mean, SD, SEM from the previous step on the blackboard. Is this mean significantly different from that of your lab partner? From one reading, determine the mean, SD, and SEM for all 4 of your 1/37 dilutions. Is 405-nanometer light visible? What color is it? Why is 405 nm suitable for measuring absorbance of NP (which is yellow)?. Does it matter whether you discard 0.1 ml from well C after mixing? After all, the concentration stays the same either way. After you have completed parts I and II, take your plate to one of the 96-well plate readers and read the entire plate twice at wavelength 405 nanometers.ĭata analysis & comprehension questions. Put 0.2 ml of diluent in well A1, which the reader assumes to be the blank. #SERIAL VS PARALLEL DILUTION SERIES#
Repeat the serial dilutions three times, so each student now has four replicate series of dilutions (first student in columns 3, 4, 5, 6 second student in columns 9, 10, 11, 12). #SERIAL VS PARALLEL DILUTION SERIAL NUMBERS#
Record the serial numbers of the pipeters you use (if they have serial numbers) else label the pipeters with tape and marker.Remove 0.1 ml from well C and discard it so all four wells contain the same total volume.

Similarly transfer 0.1 ml from B to C, mixing. Remove 0.1 ml from well A and add it to well B mix. Add 0.1 ml of the 1/37 dilution to well A and mix by pipeting in and out. In the 96-well plate, make three serial dilutions as follows in column 3 (first student) or 9 (second student).
Select one of your four 1/37 dilutions. Rinse top and bottom if it is dirty.īe careful not to scratch the bottom with a paper towel - scratches increase absorbance! Flip rinse water vigorously into the sink (ask an instructor to demonstrate) if done properly, this leaves no significant volume in the wells. Put 200 microliters of each of your four dilutions, in duplicate, in column 2 (first student) or column 8 (second student) of your 96-well plate (total 8 wells/student) II. Each student (not each pair) should make the 1/37 dilution four times, identically, to test reproducibility. What do you need to know in order to make a dilution which will meet the needs of the situation?) (Suppose you are in a research lab and you need to make a dilution of a concentrated reagent stored in the refrigerator. What do you need to know? Before making your dilution, make a list of things you need to know, and check it with your instructors. Make a dilution which reduces the concentration by 37-fold, which is a 1/37 dilution. You are provided with a concentrated stock solution of a yellow solute (p-nitrophenol), labeled 'NP Stock'. #SERIAL VS PARALLEL DILUTION HOW TO#
It is important to know how to design and perform dilutions which are accurate and which meet the needs of the situation. Reagent dilutions are needed daily in biochemical or immunological lab work.
Verify instrument performance with simple tests. #SERIAL VS PARALLEL DILUTION PC#
Download the sims 3 pc tasik game minecraft.
Pros and cons of conventional spectrophotometer vs.ĩ6-well plate absorbance reader. Determine protein concentration with spectrophotometer. Determine precision and accuracy of dilutions. Understand how to calculate optimal dilutions. Spectrophotometry & Dilutions Microbiology 542 - Eric Martz Goals: 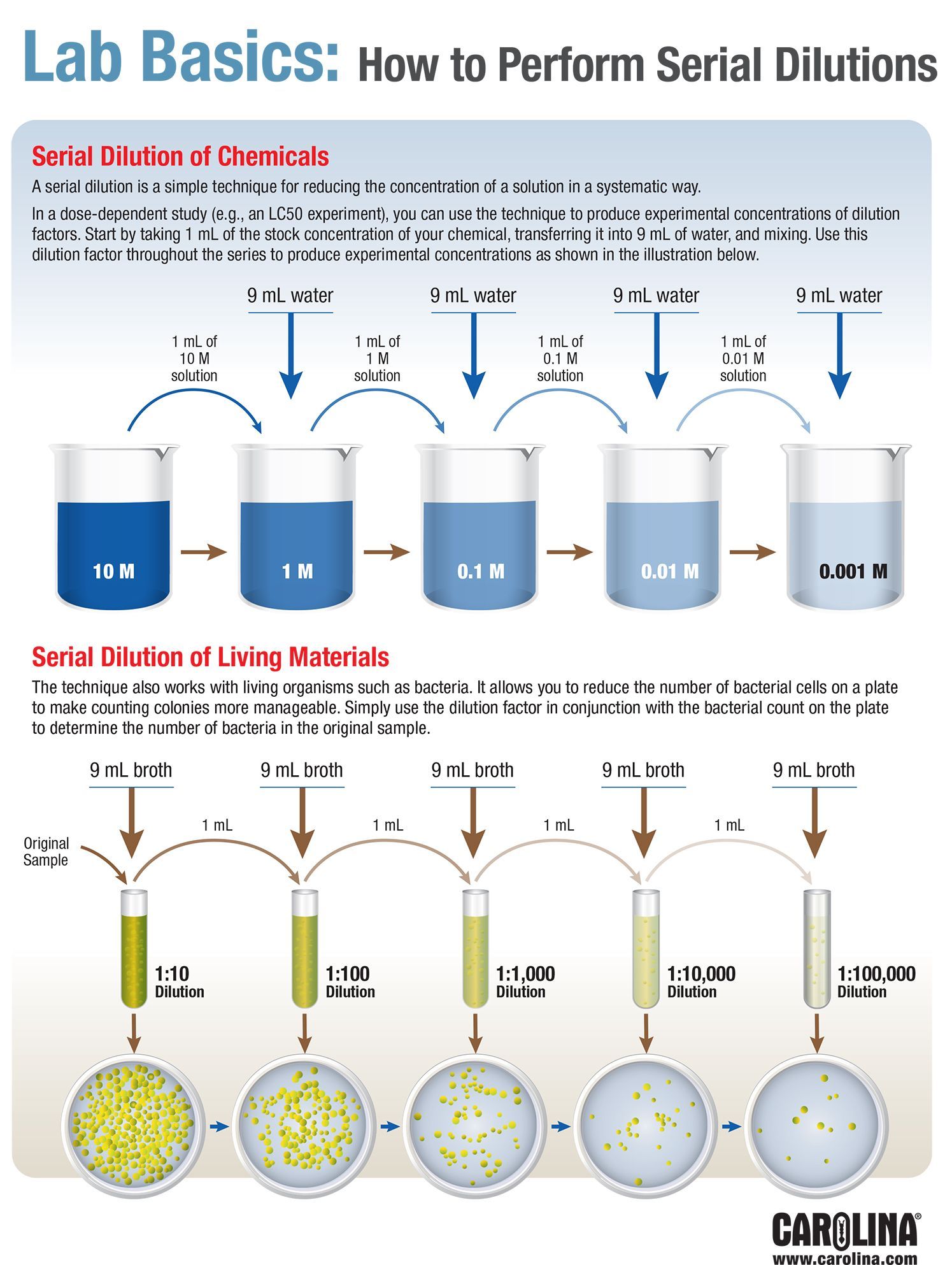
1 ml added to 9 ml gives a 10-fold dilution 1 ml added to 99ml. Serial dilution involves repeatedly mixing known amounts of source culture with (sterilised) liquid.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
